A warm wishes to all I am Dr Sarita assistant professor B Department IMT College of Science and Technology greater NOA my today’s uh live session topic is Constitution of engan these are outlines of my presentation we will study about need framing basic features structure and educational provisions of constitution of
India first of all uh we will know the meaning of Constitution Constitution is a set of laws or principles me may be written or Unwritten on which a country is acknowledged to be governed it is the system of fundamental laws and principles that describes the nature functions and limits of a government or
Another institution a constitution is an important document laying down the fundamental principles of a country the country is governed by these principles laws are also formulated according to them the Constitution is regarded as the fundamental law of a country the Constitution was adopted by the constituent assembly of India on 26th November
1949 it came into effect on 26 January 1950 after knowing the meaning of Constitution the next question arises that why we needed a constitution every nation has a constitution to guide its philosophy this constitution provides guidance and direction to the government for the safeguarding of the rights and means of
Welfare for the common people and Welfare oriented projects in all aspects of life so uh a constitution is a necessity for each Nation respective of its type of political systems first one is the Foster trust and coordination among people it specifies how the government will be constituted and the powers to take
Decisions it lays down limits on the power of the government and tells us what the rights of the citizens are it expresses the aspirations of the people about creating a good Society uh now the next thing comes that how the constitution of India was pred the constitution of India was
Formulated by a constituent assembly under the chairmanship of Dr rajendra prad the constituent assembly formed a drafting committee under the chairmanship of Dr beim edar on 29th August 1947 the draft was approved by the constituent assembly on 26th November 1949 after serious thought and wide discussion it was enforced from 26th January
195 the constitution of India took 2 years 11 months and 18 days formed a total of 6.4 CR rupees was the expenditure on this it comprises of 395 articles and 12 schedules now uh these are the basic features of Constitution and education the first one is universalization of
Education effort is being made to provide free and compulsory education for children in the age group of 6 to 14 years and we are trying to achieve this goal by such projects as s shika abyan school chalu abyan and provision of mids the next is equality of educational opportunities all children are being
Provided with equal opportunities for getting education and this opportunity is being given to everybody at the primary level and higher level also women education after Freedom special uh facilities are being given to women for education so that we can increase their enrollment in education the next is adult education
For adult education an extensive program like uh National lary mission is made in order to eliminate illiteracy from the country and to cultivate Consciousness and awokening in the people uh next is education for the handicap our government has started a coordinated educational projects for handicap and special institutions are
Being open for the Deep dumb blind and other handicap children the next is education for the SC SD and backward classes children children of these categories are given special educational facilities and reservation in education and government services are being provided vocational education the kotari commission new education policy and
Amended new education policy have La special emphasis on vocationalization of Education the next is uh education in science and technology it is s that the proper use of Technology can help to eradicate poverty and ill health and raise the standard of life of the people therefore the teaching of science and technology
Is being arranged at all levels the next and the last one is value education you all know that value education is needed for security peace development progress unity and integrity the kotari commission uh has said that the IND views towards social and moral values in present day you is the source
Of Social and moral conflicts so uh it is necessary that we make our education value based for this necessary steps are being taken now the next is pemble to constitution of India the pemble to our constitution says that we the people of India having solemnly resolved to constitute India
IND into a sovere socialist secular Democratic Republic and to secure all its citizens justice social economic and political Liberty of thought expression belief faith and worship equality uh of status and of opportunity and to promote among them all fraternity assuring the Dignity of the individual and the unity and
Integrity of the nation in our constituent assembly this 26th day of November 1949 to hereby adopt inact and give to ourselves this constitution now uh these are some characteristics of tremble to the constitution of India the opening word of the prbl are we the people of India these words mean
That this constitution has been formulated by us the people of India this has not been imposed on us by any outer people Sovereign Democratic and Republic The Sovereign meaning that our country is fully free in the internal and external policy no other country has the right to interfere in our domestic or external
Affairs and the word Democratic means that the supreme power of the political system lies with people now the next term republic is mean that the highest official of the State president is elected by the people and he is not a HRI King uh next is social economic and
Political justice as for the fundamental rights it has been declared that no discrimination will be made amongst people on the basis of social economic and political Justice freedom for religion and worship our constitution uh provides freedom to all citizens for abiding by any religion or worship system Spirit of
Fraternity our constitution emphasize on inculcating the spirit of fraternity among all Indians so that the unity and integrity of the nation can be maintained secularism it means that there is no State religion the state will be neither religious nor irreligious rather it will remain isolated from all all the types of
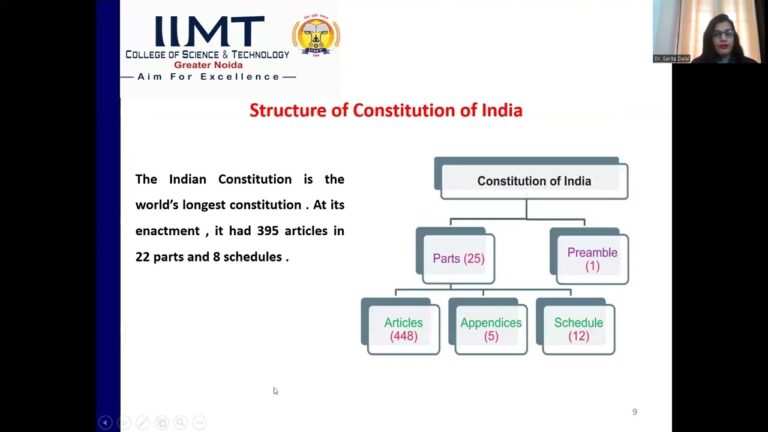
Religious ideologies and activities and religious matters the next is adoption and enactment the pemble uh to constitution of India explain that the constitution of India is ened and WR the next is structure of constitution of India this is the structure of constitution of India our Constitution contains articles parts and
Shedules it is the world’s largest Constitution at the time of its enactment it had 395 articles 22 parts and four schedules and in the present time it’s have 25 Parts 448 articles and 12 shedules now fundamental rights in India like most other democracies in the world some rights are
Mentioned in the Constitution these rights are fundamental to our life uh and are given a special status they are called fundamental rights these rights are uh preserved in the part three of the Constitution at the enactment of constitution fundamental rights had been categorized in seven classes but after the right to property
Was cancelled now there are six types of fundamental rights now fundamental rights are a very important in our constitution the significance and list of fundamental rights of the indiaia are given like uh right to equality right to Freedom right against exploitation right to freedom of religion cultural and educational
Rights and right to constitutional remedies now the next question arise that uh why are they called fundamental rights these rights are called fundamental rights because of two reasons they are entioned in the Constitution which guarantees them they are justic in case of a violation a person can approach a court of
Law the next how many fundamental rights are there in the Indian constitution uh we are discuss already and there are six fundamental rights in the Indian constitution they are mentioned below among with the Constitutional articles related to them the first is right to equality in article 14 to8 right to Freedom article
19-22 right against expectation article 23 to 24 right to freedom of religion article 25-28 cultural and educational Rights Article 29 to 30 and the right to constitutional remedy is article 32 now why right to property is not a fundamental right there was one more fundamental right in the Indian
Constitutions it is right to property however this right was removed from the list of fundamental rights by the 44th Constitutional Amendment this was because this right proved to be a endurance towards attending the goal of socialism and redistributing weth equality among the people now we list the fundamental
Rights of Indian and briefly describe each the fundamental right the first is right to equality uh the right to equality is one of the important fundamental rights of the Indian constitution that guarantees equal rights for everyone irrespective of religion gender cast race or place of birth it ensures equal employment
Opportunities in the government and Ur against discrimination by the state in matters of employment on the basis of cast religion these right uh these rights also includes the abolition of titles are well as untouchability the next is right to freedom freedom is one of the most important Idol cherished by any
Democratic Society the Indian constitution guarantees freedom to Citizens the freedom right includes many rights such as uh freedom of speech freedom of expression freedom of assembly without arms freedom of Association freedom to uh practise any profession freedom to reside in any part of the country the next one is right against
Exportation this right implies the prohibition of traffic in human beings uh and other forms of false labor it also implies uh prohibition of employment of children in factores next right to freedom of religion this indicates the secular nature of Indian poity there is equal respect given to all
Religion there is freedom of uh consigns profession practice and propagation of religion the state has no official religion uh every person has the right to freely practice his or her faith and establish and maintain religious and charitable institutions the next is cultural and educational rights these rights protect the rights
Of religious cultural and linguistic minorities by facilitating them to preserve their Heritage and culture educational rights are for ensuring education for everyone without any discrimination the next and the last fundamental right is right to constitutional remedies the Constitution uh guarantees remedies if citizens fundamental rights are violative the government cannot infering
Upon the Cur anyone’s rights when these rights are violated aggrevate party uh can approach the courts citizens can even go directly to the Supreme Court which can issue rits for enforcing fundamental rights now these are the fundamental duties in our constitutions there are 11 fundamental duties in our constitutions the first
One is abide by the Constitution and respect national flag and National an follow Idols of the freedom struggle uh protect sovereignty uh and integrity of India defend the country and render National Services when called upon developing the spit of common Brotherhood preserve composite culture of the country preserve natural environment develop scientific temper
And Humanity uh Safeguard public property and avoid violence strive for excellence in all spheres of Life uh the last fundamental duty is according to the 86 Amendment when parents and Guardians are supposed to uh educate their vs in the age group of 6 to 14 years now uh directive
Principles a chief characteristics of the Constitution of India is that some principles have been charted uh about the name of directive principes of State policy for guiding the state these directive principles have been mentioned in the fourth part and article from 38 to 51 of the Constitution now there are five
Classifications of directive principles the first classification is it is related to Economic Security uh next is related to agriculture cottage industries and and gram PCH uh related to health education and environment related to justice social welfare and protection of monuments and related to International Peace and security now these are uh educational
Provisions in our constitution uh like article 21A article 21A uh in the Constitution of India to provide free and compulsory education of all children in the age group of 6 to 14 years as a fundamental right in uh such a manner as the state may by low determine article
281 no religious instruction instruction shall be provided in any educational institution all maintained out of statements article 292 no citizen shall be denied admission into any educational institutions maintained by the state are receiving aid out of state funds on grounds only of religion race cast language or any of
Them uh article 31 all minorities whether based on religion or language shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice the next is article 41 it directs the state to secure the right to work education and public assistance in certain cases such as unemployment old age sickness and
Disablement article 45 talks about the provision uh for free and compulsory education for children it states that the state shall Endeavor to provide within a period of 10 years from the commencement of this constitution for free and compulsory education for all children until they complete the age of
14 years uh the next is article 46 the state shall promote with special care of educational and economic interest of the weaker sections of the people and and in particular of the scheduled cast and the scheduled tribes and shall protect them from social injustice uh next is article 343 the
Official language of the Union shall be uh Hindi in D nagari script in article 350 uh a facilities for instruction in mother tongue at the primary stage it provides that it shall be the Endeavor of every state and of every local Authority within the state to provide adequate facilities for instructions in the
Mother tongue at the primary stage of Education to Children belonging to linguistic minority groups article 351 uh of the Constitution provides that it shall be the duty of the Union to promote the spread of the Hindi language to develop it so that it may serve as a medium of expression for all the
Elements of the composite culture of India thank you so much
source