Neoplasia where we on now you know neoplasia is a big bugaboo in fact that’s what’s being taught as we speak back in my school we dedicate 5 hours of teaching it in a school and it’ll be well taught and he’ll forget it okay it’s the nomenclature that get
You and I just don’t understand I guess well I I guess I should because I’m a pathology because this is the second nature to me to know this stuff but I don’t get why students have so much trouble with nen clature that seems to be the big Bugaboo I mean most would not
Be able to tell me the difference between farom and a sarom leukemia and Aloma have no idea most people most medical students where they if they do they forget it real fast so let’s make sure you got it huh because very important okay so we have benign and malignant huh
And the main difference really to get all the other crap about whether it has a capsule no Capsule that’s all bull crap the main thing is benign usually doesn’t metastasize malignant has the capacity to metastasize that’s the big difference between benign and malignant there are exceptions to everything okay
Uh I know a tumor that’s benign that metastasizes okay and it’s an invasive mole that’s a benign tumor that can metastasize to your lungs but it’ll go away so there’s a benign tumor that can metastasize basil cell carcinoma most common skin cancer invades but doesn’t metastasize so there are exceptions but
In general the main difference between benign and malignant is that benign doesn’t metastasize malignant does forget all the rest of it okay I’m going to scul through some nomen clature here’s the uterus and you got these little dudes in there name me lioma here’s the board question the most
Common benign tumor in a woman is most commonly located in which of the following organs uterus okay because that most common tumor is a lamoma which is a tumor of smooth muscle the term fibroids is often used bad term and oid means looks like fibrous tissue but isn’t and that’s true because it’s
Smooth muscle okay I guess it’s because they become so hard okay that they give they they uh they look like scar tissue but they basically derive from smooth muscle do they become Lomas no there’s no transformation okay this is the most common benign t in a in a man and notice
It’s yellow uh yellow I’ve got a couple of them right along my my elbow right in here and move around a little bit what is it lipoma lipoma is the most common benign tumor in a male most common benign tumor in a woman it’s liom and uterus okay we have uh tumors benign
Tumors of glands they call those adenomas here’s the adrenal is an adenoma of the adrenal you can see by the thinness of the adrenal cortex that this must be functioning that’s right it could be making cortisol what would that suppress act what would that screw up in the adrenal cortex facular and reticularis
Would undergo atrophy that’s pretty much what’s happening here so this is a functioning adenoma secreting cortisol producing Cushings in a patient what if it was uh and arising from the what if it was making mineralic corticoids that’d be con syndrome okay so what would that be doing would be causing it would be
Causing atrophy of which section zone of glosa hey guys if you Haven to figure it out the three layers GFR glal filtration rate glosa ficula reticularis glosa salt the facula glucocorticoids reticularis sex hormones very simple okay very simple make sure you know that they actually have diagrams
You know with arrows pointing to these different things okay this the tubular adenoma this is the most common precur lesion for colon cancer looks like a strawberry on a stick look at it because you’re going to see it you see something looks like a strawberry on a stick
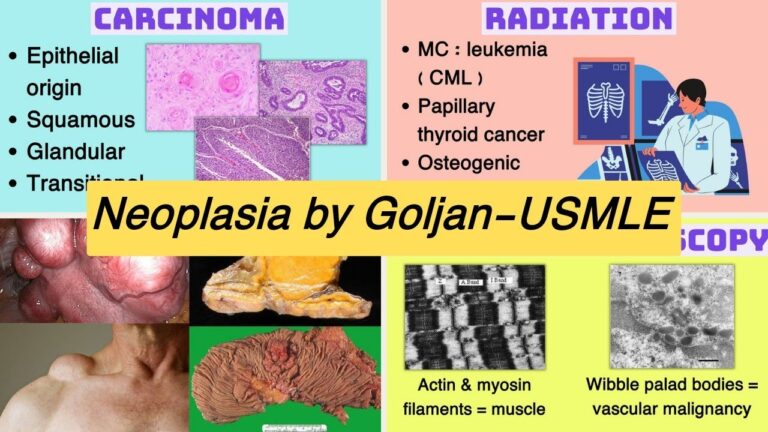
That’s a tubular adenoma it’s a precursive for colon cancer okay carcinoma saroma carcinoma is a malignancy all of this is in your notes I see no reason for copying anything down I honestly don’t you’re going to miss the important points carso is a malignancy of epithelial tissue we have three epithelial tissues squamous
Glandular transitional okay this is squamous carcinoma look at it don’t be looking down look at this how you going to recognize it these dudes these little swirls of increased redness in air called squamous pearls they are on everyone if they’re going to show you Squam with cancer they always show those
Every student in this room should know s Cancer all you got to do is recognize these little red things that little swirls nice and dark nice nice bright red squamous srl squamous cancer okay that’s one type what are these things they glands you can see their glands they’re round and they got
Something in the middle glands adinal carcinoma so if they were to show you a picture of an adinal carcinoma they would show glands and they would be things inside not heart to identify this right here is Transitional cell oroma okay these would course would come from the genital urinary tract the
Bladder okay the urer the renal pelvis without transitional epithelium so those are your three carcinomas squas adinal carcinoma transitional cell carcinoma okay with me so far okay some other terms diagnosis M melanoma first step in management excision okay this is a malignancy of the um melanin of the melanocytes what’s the benign Legion
Called anas anus is a benign version melanoma is a malignant version derived from the melanocytes okay it’s the most rapidly increasing cancer in the United States it’s not that’s not to say it’s the most common cancer I said was the most rapidly increasing cancer in the United States okay they’re S100 antigen
Positive they are opud tumors opud amine precursor uptake decarbox what does that mean okay it means they of neural secretory or neuroc Crest origin it means they have when you do electron microscopy which I have another picture of when we do lung uh they have neuros secretory granules on electron
Microscopy S100 antigen is an antigen that we use for staining things of output origin of neuroc Crest origin most not all will take up that stain so they’re part of the output tumors and they’re all up here for you except for a few so melanoma is an output tumor this
Is the small C choma of the lung okay that’s an output tumor neural secretory tumor it’s less malignant counterparts called bronchial carcinoid that’s an output tumor this a carcinoid tumor of the tip of the appendix that’s an output tumor okay this is a neuroblastoma in in
A medulla in a child it’s an oput neuros secretory tumor they say I don’t think they has stuff like that oh really and what about the two two-year-old that had nodules all over their skin they bioed him so these small hyperchromatic cells which were S100 antigen positive that’s it
That’s all they said and they said where’s the tumor coming from Adrenal medulla was a neuroblastoma metastatic to skin so don’t tell me they don’t ask questions like this they do they do so this pretty nice because it really puts most of the output tumors except I don’t have a Broncho coronoid
Up there sarus sarom is a malignancy of meenal tissue not epithelial meenal okay here’s a bone okay this is the metaphysis you can see that it’s split up this little periosteum so an x-ray would show codman’s triangle there because this particular tumor makes bone you can actually on an X-ray see what
Looks like a Sunburst appearance okay diagnosis osteogenic saroma what do you think osteogenic means bone making saroma see this picture this is on boards they said this is a biopsy of a patient a little girl that had a a a a mass a a necrotic mess coming out of her
Vagina so they biopsi it and this was there and it was a vimentin negative um kin negative and Desmond positive diagnosis diagnosis and Brian arrived Myoma Bri R you should have known that why stations guys those striations of muscle this is the most common saroma children it comes out of the vagina of
Little girls and out of the penis of little boys okay so what’s a saroma of a smooth muscle name it liom saroma strided muscle rabdom sakom uh fat lipos sakom very good so those are malignancies of meenal tissue carcinomas epithelial tissue okay I put these two together because
You confuse them frequently who can tell me what this movable Mass is at the angle of the jaw no mixed tumor mixed tumor it’s okay mixed tumor and what what organ is it in P it it’s your most common overall salivary gland tumor usually benign AAS malignant when
It says it’s mixed it means it has two histologic different types of tissue in it but they deriv from the same cell layer it’s not a Teratoma which is why they try to get you this is this is a Teratoma how you know cuz there’s a to there’s hair there’s a comb underneath
There there’s a toothbrush underneath there God would never produce a Teratoma with teeth and hair without supplying the things to take care of it keraton is derived from all three cell layers ectoderm endoderm maderm you all know the question on cystic ponas of the ovary 16-year-old girls sudden on a right lower quadrant
Pain they always make it on the right lower quadrant why they want to confuse you with appendicitis Crohn’s disease ectopic pregnancy folicular cyst and the whole bit you have to know the whole differential for right lower quadrant pain then they say to do an x-ray and it shows some calcifications in the pelvic
Area voila okay you’re dealing with a cystic ptera okay the the calcifications could be bone or could be these teeth okay that’s a Teratoma all three cell areas mixed tumor two different types of tissue same cell layer pared gland uh another name for these types of things of germ cell tumors because they
Are toy potential and they have a tendency of staying in the midline the ovaries are reasonably midline okay edusum is right in the midline so teratoma is commonly developed there in the pine gland uh is is midline so they talk about midline tumors the teratomas which are germ cell
Tumors okay leukemia lyola there’s no there’s a reason why I put these two together so that you can get this okay this picture was on 8 million boards I was teaching in Washington DC when the first computer-based exam was given and it was one student that actually took that test that day the
First day of lecture actually came back and of course he was surrounded by people okay and so of course I got him alone okay you have any hematology yeah how many pictures two I’m going to tell you what they are oh no you can’t tell me what they are sure I’ll tell you
Exactly what they were all right go ahead there was a hour rod and a Milo blast his eyes went open like this because it was this picture there’s your hour rods that’s a Milo blast and so the second one was a hypers segment and nutrifil that’s right okay be
Deficiency if I had to pick two pitches it would be the two I pick two okay that’s the way they did it so you’re almost guaranteed seeing this for leukemia and the hypers segmented nutriful for full8 B12 deficiency a leukemia is a malignancy of stem cells
In the bone marrow and like all cancers they can metastasize out of it and always do lymph nodes you have generalized lymph adenopathy hepo splenomegaly guaranteed in other areas of your body so they derive from stem cells in the marrow and metastasize a malignant lymphoma is this malignant lymphomas arise from lymph
Nodes and because they are malignant they can metastasize wherever they want including bone marrow not all do but they can so they can metastasize to the same place as leukemia does but one arises from the blimp node the other one arises from the bone marrow that’s leukemia versus
Lymphoma now who can tell me the most common sight in the body for a lymphoma not developing in a lymph node the stomach is the answer to that question most what they call extranodal outside lymph node primary lymphomas occur in the stomach our little friend helico back to pyloric can produce
Them okay this one you should get this one you should get what’s the second most common location hint it’s a lymphoid organ in the GI tract pyes patches where are pyes patches located they’re terminal Ilan that’s the second most common sight are you with me you better be because this is big
Time so I put these two this is good mix Tuma versus teratoma leukemia versus lymphoma this by the way is your most common lymphoma it’s called a folicular bell lymphoma and it’s an example of knocking off an apoptosis Gene there’s a 1418 translation of a heavy chain and
What happens is when you get that translocation the B cells uh make this bcl2 thing product which inactivates the apoptosis Gene in the B cell remember we said it’s involved in programed cell Deb if you knock off that one the apoptosis Gene then that cells immortal so it’s the it’s the question
On boards for an A A inactivation of apoptosis Gene cancer is the most common of all the lymphomas that’s a b lymphoma okay right now we’re just giving you just little little Histories on these things and just names that’s what we’re interested now we talk about this another time and this another
Time all right trop blastic tumors these are tumors we see in pregnancy but of course males can get them and have nothing to do so that’s non-gestational you all should know what this is cuz it’s on every exam what is it it’s a hydraform mold it
Looks like a bunch of grapes that’s what it is you all know that hydrated or form moles present in the first trimester with signs of preclampsia so any patient that has hypertension proteinuria uh and edema um in the first trimester you’re going to do an ultrasound and you’ll see that you have
Uterus too large for gational age with snowstorm effect from the ultrasound that’s class CLC mole this happens to be a complete mole which has the highest tendency for going into this Legion that’s called Coro carcinoma a mole is benign tumor of the chonic villis chonic Villi are lined by
Trophoblastic cells they include sensial trophoblast on the outside that’s the part that has contact with the blood from which oxygen is going to be extracted you better listen on this okay because they ask you the direction of how all the layers that oxygen goes through in the chonic villis they
Do and under this cissal trophy blast is a cyral blast okay then you have the little Wharton jelly in the chonic villis then you have a little vessel that’s in the middle of the chonic villis which eventually becomes the umbilical vein which is the one that has
The most oxygen of all the vessels in the fetus all of this is on boards guys so the hyad foro is a benign tumor of the whole chonic villis that’s why it looks like grapes okay because they’re all dilated up and when you have a coral coroma that’s not a malignancy of the
Chonic villet it’s a malignancy of the lining of the chonic V the sensial tropho blast and the cyot tropho blast which of the two makes hormones guys cial tropo blast name them beta HCG what’s the other one it’s the growth hormone of pregnancy human placental lactogen human placental lactogen is the growth hormone
Of pregnancy it gives amino acids from Mommy to the baby and glucose from Mommy to the baby both of those are synthesized in a sensial tropho blast these are malignant but what’s interesting is when they’re gestationally derived even though the metastatic to lung which is their favorite site they be respond incredibly
To chemotherapy like methyl trexate chlorambucil and they go away so it’s an example of a highly highly malignant tumor but it it’s almost you almost get entire remission with just chemotherapy that’s wonderful that’s good break 10 minutes all right 10:00 okay we’re doing reasonably good okay all that ends
In is not necessarily benign okay so take melanoma if you just say that you know and You’ say that must be benign Tom of melanocytes no it’s a malignant melanoma lymphoma so that must be a benign tumor of the lymph nodes okay no it’s a malignant tumor so all
That enen is not necessarily malignant also all Enz andom is not necessarily a neoplasm and I’m showing you the two good examples of that this is called a hamartoma a hamartoma is a overgrowth of tissue that’s normally present than that area and the one that you all know is a
Bronchial hamartoma basically all this is is cartilage it’s benign cartilage and it presents a solitary coin lesion in the lung which makes you wonder about whether it’s a granuloma or something of that nature but it’s a hamartoma so they’re not a neoplasm the pop of P Jer syndrome is a
Hamartoma it’s not even a neoplasma that’s why there is no really increased risk for colon cancer and P Jager syndrome because the pops are not on non neoplasms the hyperplastic pop which is the most common pop in the entire GI tract is a hamartoma so it’s not even a
Neoplasm okay all right this one here is a section of stomach and in the uh in the muscle wall of the stomach is benign pancreatic tissu does that belong there yes or no no so when you have benign tissue in a place that shouldn’t be that’s called a chisto or another name
Heterotropic rest either one of them okay me diverticulum is a classic example I mean what’s the most common complication of the meal diverticulum bleeding from what well usually either gastric mucosa that’s ulcerated or sometimes pancreatic tissue causing the ulceration should gastric mucosa be in a meal di reticulum I don’t think so
Because that’s in a small bow remember that’s roughly 2 feet from the ilal valow that’s an example of a heterotopic rest should pancreatic tissue be in it no but it is so that’s another good example of a heter topic rest so hamartomas are are um non-neoplastic lesions and therefore have no potent
Potential for uh producing cancer okay so let’s talk about the big word m or the big word c uh cancer you know one of the big misconceptions is that you know increased mitotic great meets cancer no I mean we have lots of cells in our body that are mitosing right now that doesn’t
Mean we have cancer mitosis are part of the growth of the cell cycle the thing that really makes a mitosis malignant is this see that’s not the normal uh that’s not the normal mitotic uh uh configuration this says this says uh this probably has is four a 4N cell this
Has more uh chromosomes in it than normal when you have an atypical mitotic spindle that’s cancer so an increase in mitotic rate doesn’t really mean anything but when you have typical mitotic spindles that us you relating to the fact that they’re annup Ploy they have more than the the normal 46
Chromosomes they might have 63 or whatever that’s malignant okay also remember that the C quanon that means the key thing that determines whether something is malignant is his ability to metastasize a couple other things I have listed down there for malignant cells they have usually a longer cell cycle
Than the cell from which they derived you do you do need to know about that this is a memorization thing but they throw it every now and then they say how many doubling times does it take before you get a tumor that you can detect clinically the answer is 30 30 doubling
Times means 30 times going through the cell cycle and you get a tumor that’s about uh one sontimeter in size okay 10 the minus 9 in Mass okay so 30 doubling times is something you want to remember is that when it’s when a tumor can become clinically detectable a malignant cells are
Immortal I mean say they really can’t die they can live forever in tissue in fact we use burket lymphoma cells in um in uh as a test for immune complexes okay so we can grow Burk lyoma cells in culture they’re Immortal they don’t like each other so okay they kind of don’t
Stick to each other they lack adhesion that’s important because if they if they were stuck to each other then how are they going to infiltrate tissue so they lack adhesion they don’t like to stick to each other said leave me alone I want to just I want to burrow through this
Tissue myself okay I don’t want anyone impeding me okay they have very very s simple biochemical systems usually anerobic metabolism they have lots of enzymes they they love they have to have proteases because that’s one of what’s going to they’re going to use to break through the tissue
Proteases okay uh they’re going to have to have collagenases to break through that basement membrane so they have to have those kinds of enzymes to do things like that okay those are the key things that that make a malignant cell malignant metastasis three three modes of metastasis lymphatic hematogenous
Seeding now this big misconception here too now remember we have carcinomas and we have sarcomas how do carcinomas usually initially metastasize lymph nodes they drain to their Regional lymph nodes so for breast cancer that’s the axillary nodes they can also go to the internal mamories if they want for colon
Cancer would be the nodes right right around it for sage cancer the nodes right around it so they go to the local lymph nodes what part of the lymph node the subcapsular sinus okay and this is showing uh this is showing a mcken cells in a lymphatic here and then showing
Here a lymph Noe that has been partially replaced by a malignant tumor okay malignant tumor so they first go to lymph nodes as a rule but don’t forget if they can get through that lymph node and go into the eeper lymphatics and that drains into to the thoracic duct
Which jumps into the subclavian then they’re hematogenous so don’t think that carcinomas are not hematogenous spread of course they are and when they’re hematogenous that means theyve already got through the lymph nodes and so when they hematogenous is when they can go to Bone and liver and other places okay so
Don’t forget that you know carcinomas can be hematogenous but usually first they go to the lymph nodes in a sense that’s good because if we can feel that lymph node by clinical exam we can maybe pick up that cancer at an early stage unlike sarcomas which don’t like going
To lymph notes they just like going right through blood vessels right there and they and they usually characteristically metastasize hematogenously that’s why the the lungs and the bone are such common sites for sarcomas okay they don’t usually like going to lymph nose so those would be a little bit worse wouldn’t they because
They go hematus right off the bat okay they don’t give us any hint that they’re there because they don’t like going to lymph nodes and the Practical practicality of that is is that if you have let’s say an angio sarom of the breast would you do a radical dissection
Of the axilla no why because an angio sooma doesn’t go to lymph noes you do simple mastectomy if it was a breast cancer though a carcinoma you would take the you know the breast or you do a lumpectomy and you’d sample a couple limp nose would do a complete dissection
Okay that would be part of it because carcinomas go there okay you understand so there’s practicality in knowing that okay so this is lymphatic spread you can see it to a lymph node here this is tumor in a vessel now I I know my pathologist friend knows I’m going to
I’m trying to pass this off as sakom and he knows that it ain’t but um any R sakom like to go in a blood vessel this is a blood vessel and here’s tum in a blood vessel actually this is a carcinoma that doesn’t know it is it’s a folicular carcinoma the thyroid there
Are some carcinomas that say no I don’t I don’t I don’t always want to go to lymph nodes I want to go to hematogenous okay and so one classic one is the folicular cancer the thyroid doesn’t like to go to lymph nodes it thinks it’s a sacoma okay kind of a transvesti thing
Or whatever you call something like that okay uh renal adoc carcinoma you know likes to invade the realen vein I mean it shouldn’t be doing that well I like it why do you like it I just like it okay okay and it determines your prognosis too in fact I’ve seen uh renal
Vein I’ve seen it go all the way up the renal vein and up to Interior V CA I mean it like so much hpal cellular carcinom is always invade vessels so there’s exception to every rule I’m saying okay but in general carcinom is first go to lymph nodes and then have
The potential for becoming hematogenous sarcomas usually don’t like lymph nodes and go directly hematogenous which makes them dangerous there are some sarcomas that do go to lymph nose but you don’t need to know them seeding seeding is a concept of like seating farmer throws out seed and wherever that
Seed lands it expects it to go and Barrow into the dirt and out comes the plant okay and so when we have cancers that are in cavities a classic example ovar ovarian cancer they have a tendency of seeding little malignant implants okay see most ovarian cancers are surface derived cancers so that means
They derive from the lining around the ovaries and so you can see it’s very easy for them to seed throw out malignant implants of small little pieces of cancer they go over the momentum and into the Douglas pouch of Douglas okay uh with which is uh just posterior to the uterus and just
Anterior to the rectum we can feel that by rectal exam the pouch of Douglas is uh to a woman as the prostate gland is to a man when you do a rectal on a man you press forward that’s your prostate you’re feeling when you do a rectal on a
Woman you press forward you’re feeling the rectal pouch of Douglas which we’ll show you when we do GYN okay very important area because it’s the most dependent part of a woman’s pelvis that’s where things like unclotted blood go and erupted ectopic that’s where in the metal lyph plants go
In endometriosis that’s where seeding goes in ovarian cancers the PCH of Douglas a very important anatomic location been on many many boards so seaing and this is an example of novarian cor and that seated to the amum okay so it actually can invade uh you can actually see it in the plural
Cavity for example if you have a perly located lung cancer it can get to the plur can see through the plural cavity okay and you can see little implants along G blastoma multi forming most common primary malignancy of the brain in adults can seed into the spinal fluid
And implant the entire spinal cord so can a meal blast stone and a little child do the same thing okay seeding that’s the concept so we have so we have uh lymphatic hematogenous and seeding as the three mechanisms for metastasis okay now I want to make sure
You understand this concept and that is if they ask you about you know most common Cancers and stuff like that could you please when they ask something like that first they ask yourself the question is metastasis more common than the primary cancer in most cases metastasis is the most common cancer in an
Organ okay not a primary cancer and I’ll give you an exception to that renal adoc coroma that is the most common one not metastasis to it when we talk about lung most common cancer most common cancer in the lungs metastasis and unfortunately it’s breast cancer that’s the most common that’s the
Most common cancer in the lung it’s breast cancers that means that women uh are more likely to when they uh to uh to get the have metastasis too long bone most common cancer bone is not multiple myom osteogenic soc no no no metastasis and unfortunately again the most common
Cancer that metastasizes the bone is rest that’s because that stinking Batson system the bats system it’s a Venus complex that goes from the base of the skull down the down to the sacrum it has no valves in it and and the little tributaries communicate with the vnea and they also
Little tributaries go right into the vertual bodies then they collect all together on the inside right around the spinal cord area and go back up so there’s a horrible little system there and so you take a woman with a breast cancer for example she maybe got a little plug of
Tumor in an intercostal vein she goes and picks something off the ground and she dislodges that little piece of cancer from the vein to the vena into the bats and plexus and the vertebral body 3 months later she’s complaining of low back pain all of a sudden she staged four
Cancer just by bending over stinking bats and system the most common bone metastasized too is the vertual column second most common is the lumbar area the vertial col second most common area is the head of the femur any good pathologist knows that an old person gets a femoral head remover always take
A sex or to because thinks metastasized to it woman breast cancer I’ve seen breast cancer in the fal head that they thought was was related to degenerative arthritis it was breast cancer that caus the problem okay so remember that most common what do you think the most common
Organ metastasize to is lymph noes that one you actually could figure out because carcinomas are more common than sarcomas carcinomas like to go to lymph noes that would be the most common metastasize too this one will get you all ready what’s the most common cancer of
Liver pastas is what do you think the most common primary is you want to say colon don’t you it’s not col it’s U lung most common cancer metastasize since liver is lung don’t believe me look in sabiston sexbook surgery and have this big table with 100 something thousand
Autopsies and by Far and Away lung beat colon lung beat colon as the most common uh cancer metastasizing to liver second would be colon because of the portal vein drainage okay here’s another one where would a testicular cancer metastasize to First please the parotic lymph nodes why not the why not the
Ingal lymph nodes because remember it derived from the abdomen and then descended into there see those are questions they ask in anatomy guys okay they they they take a clinical bent on on a question that related to knowing that the the the testicles originally from from the abdominal cavity and then
They just descended into the tesel so if they’re malignant like a seminoma first place is not the inguinal nodes in first place would be the parotic notes from once they came okay what about that left super cicular node what do you think of that with that metastasis that’s called veral
Node most common primary stomach there you go they don’t say V cows no they just say there’s a nass the left super clavicular no they do not give actual names to these things but is ah V cows and someone with weight loss and epigas distress duh stomach
Cancer plasticizing I want you to look at this please this is a radio nuclei scan which is the best test for looking for bone Mets everywhere you see black except that urine down over there is metastasis this poor woman with breast cancer this doesn’t in solidify in your
Head that the most common bone metastasizes to is the vertual column I don’t know what will this entire brao column is full of cancer and there’s your pelvic cural notice you’re going to get a little bit on the chromio clavicula area too now we have metastasis at alytic we
Have metastasis that are blastic liic means they they they break bone down okay you all know that multiple myom has these nice punched out Legions you want to know why all malignant plasma cells have interlan one in them you already know what interlan one is got another name for it osteoclast activating Factor
So you already know the mechanism for that okay so we have liic and so we can get pathologic fractures from that we can also get if they a litic what metabolic abnormality hypercalcemia there you go okay then we have some that they go in the bone and induce an osteoblastic
Response take this for example I mean that’s bone you can see it’s dense okay so I want you to tell me what enzyme would be elevating in this patient Alin phosphates and I want you to tell me is this a male or a female play odds male with what cancer prostate cancer which
Is almost always osteoblastic and because it’s making bone it’s going to release Alan phosphatase most common location for metastasis is a lumbar vertebrae actually want the board question got an 80-year old man with lower lower lumbar pain with point tenderness okay well they said what’s your first step in management they said
Bone scan they said PSA prostate specific antigen they said uh uh trans ultrasound what’s your answer your finger rectal exam was the answer why that’d be stage four disease which means that definitely the prostate is going to be palpable so that’d be the simplest easiest thing to do put your finger in
There hand check you know that’s it and of course you are going to do a PSA you are going to do a scin but the first step in management is the obvious the cheapest your finger with something on it C I can’t tell you how many people pick
PSA prostate specific antigen bad error or radi nucle bone scan to make sure that’s not lumbar metastasis that’s great you’re going to be doing that but you should have done a rectal before you with me good these are litic metastases you can almost see that look at how that vertebra is
Collapsed so you have lucencies Lucen sees you know where there’s an absence of bone with liic metastasis whereas in blastic you’ll have entities on regular x-ray okay all right now just a point this is the CT scan of the liver and you notice there’s multiple defects I want
You to remember this and do not forget this this is a general statement if you see a growth specimen an x-ray of something I don’t care what CT MRI a gross whatever it’s got multiple lesions in it it’s metastasis for your intense and purposes don’t pick abscess you know
Or whatever it’s metastasis don’t pick primary cancer primary cancers usually aren’t like this usually they’re within one area maybe another area but not all over the place so if you see any grow specimen any x-ray with multiple lesions in it it’s metastasis just find out where in that that choice that deals
With metastasis understand do not pick anything denying ever all right here’s just examples of other places metastasized too there’s the brain what do you think the most common cancer your brain is metastasis what’s the most common cancer killer in men and women lung cancer therefore what
Do you think is the most common primary site for cancer in the brain primary lung there you go okay this is liver you already know that’s also lung here’s lung what’s the most common cancer in the lung metastasis and what’s the most common primary breast okay this is the
Adrenal gland when you think the most common tumor metastas to adrenal is lung that’s why they always do CTS of the high lymph nodes and they have the adrenal glands in the staging of all lung cancers because they go so commonly to adrenal glands okay and of course this is bone
Is this litic or blastic it’s blastic so what is it most likely cause prostate cancer there you go all right stains well I’ve already mentioned one Desmond I remember uh intermediate filaments uh Desmond is a wonderful stain for muscle and that’s why uh they use that when they think they have a
Muscle tumor like an embal rabdom monoma they do that we have stains for keratin most carcinomas have a keratin in them and so we stain for that we have stains for just about everything and we use them in helping us identify different kinds of tumors okay so that’s what I’m
Going to say on that electron microscopy is not used very commonly in pathology only sometimes when we have no idea what the thing is the stains don’t work all the different special things and all that don’t work we sometimes have to do electron microscopy and see if that’ll
Help us okay uh sometimes like for example if we had an output Tuma what would we see neuros secory granules if we had a histi acidic tumor like let’s say histiocytosis x letter of sewe H lris what will we see bbic granules okay because they’re characteristic and what
Would be the cluster designation that we would see cd1 there you go okay if we had muscle what would we see we see actin and my filaments okay if it was a if it was a vascular malignancy we’d see wable pad bodies these are the structures that
Have V willbrand factor in them we can actually see those things so we know the things of is of of endothelial origin are you with me this is how they get at histology guys histology is the least important thing on the exam but the way they ask the questions is in
Relationship to how we use histology in making diagnosis in pathology that’s how they use it and don’t forget get the Gap Junctions got know all the Gap Junctions you know which ones communicate which ones don’t and all that stuff okay now this is the most important part right here ancle Genesis
I’m going to make this as simple as I can why because I can’t understand it all because there’s just so much to it but I think what I’ve got is more than enough for this sport I’m going to be very simple on this first of all whenever you study something always get
The big picture first don’t start delving into little picky f that’s why you’ll never end up with a knowledge of anything by I can always tell when you don’t know how to study you open up a book and you start underlining right off the bat you have no idea how to study
That’s not the way you study because you’re already starting to get get picky facts the way you study is to get the big picture first that means you don’t underline anything you just read it through fast at the level of a novel or a little slower than a novel get the big
Picture and the big picture to me is definitions knowing the definitions of the different things that’s the big picture then you go back and and study for you know the mechanisms and stuff like that got to have a big picture no big picture you’re screwed so what would be a big picture
For example tissue hypoxia big picture would be esia hypoxemia hemoglobin related problems uh um uncoupling of oxidative phosphorilation uh that that’s the big picture okay you don’t know that you’re screw you don’t know tissue hypoxia okay got to do big pictures first so here’s the big
Picture the way we’re going to do this by I don’t know if you understand some of you may not have in your countries and probably you’re lucky fraternities and sororities this country and the colleges they have all these things it’s the way you going to remember ancle
Genesis okay so if I was going to go want to get into a fraternity in college I have to be initiated so the first step in malignancy is initiation and that means mutation it has to be mutation there’s always kinds of mutation we’ll learn them in a second
That’s the first part of going into fraternity of SAR you have to go through initiation do stupid things but for anco Genesis it’s a mutation okay we like you you did all the stupid things please come into our fraternity okay so now you’ll be promoted okay you are promoted
Into the uh into the fraternity so promotion is the second step of anco Genesis that’s where you make multiple copies of that mutation remember from going into the G1 or the S phase you got a mutation in there and you start going through that cell cycle bad news you’re
Making multiple copies of it that’s that’s uh promotion okay and then you’re in this fraternity and you are really a really really good say we want to make you President we want to make you in charge of the whole thing so you progressed in that fraternity or that
Sority and now you’re a leader that’s the third step in anco Genesis is progression and what that means is that different different kinds of cancer cells are have different functions it’s it’s basically a community of Mal cells that has one purpose to kill you okay okay you just see this big
Collection says Okay who wants to stay where you are me okay you’re the couch potato you stay here who wants to invade right where you are me okay so they give special things to be able to invade who wants to go to the lung me okay and they’re giv special things with
Receptors to hone in on a lung yep that’s the way it works I mean they all they even have some who wants to resist the chemotherapy they’re going to throw at us me okay and so they have those that can actually you know resist the chemo before you even throw it at
Them that’s why culturing cancer cells is the big thing now they’re kind of doing like they do with with bacteria you know they put the sensitivity plates the curvy Bower you can do that with malignant cells now they do with melanomas they take your tumor they put
It in the uh on the in the culture medium and they can put discs that have different chemotherapy agent s and seea kills them and then it can give you the exact chemotherapy agent and it’ll kill it that’s where it’s going but unfortunately they can’t do that for every Cancer otherwise that
Would be the best way this is called progression so could you please tell me what the stages are in order please what’s the first stage initiation what does that mean mutation okay what’s the next step promotion what does that mean dividing it making multiple copies then what’s the last
Stage progression what does that mean just sub specializing okay good that’s the big picture now let’s go and start start getting into um the finer points well we have two sets of genes that are involved in cancer one we have those that are involved in the growth process
Those that are involved with self cycle related things you’ve already been introduced to some of those okay um then we have those kinds of genes that kind of like monitor things suppress things so we have groups of cells that are involved in the normal growth cycle and
Then we have other types of genes that are involved in suppression those are called suppressor genes okay those are the two big sets of genes now you all know and you should have had this in cell biology already let’s take things that are involved in uh trying to get a cell to
Divide well first of all we have growth factors good examples epidermal derived growth factor okay well there are certain what they call Proto longa genes these are cancer these are genes are cancer genes but normally when they haven’t been activated they actually serve a normal function in a normal
Growth process that’s why they’re called Proto anagen when they become enogen that means that they’re bad they are cancer producing genes um and so we have certain protooncogenes that code for growth factors a good example Cy sis is a protooncogene its only function is to make the growth factors all growth
Factors have to hook into a receptor just like all hormones have to hook into a receptor okay insulin hooks into a tyrosine Kates receptor on atopos and muscle everything has to hook into something receptor okay so we have certain Proto ancoines whose main job is to make receptors so the herb2 the
Classic one for breast cancer is an example of a of an anene a Proto anene who cods for receptor okay cods for receptor another one’s R the r which is in men syndromes men one men two okay Men 2 a 2 B I just love it Men 2
B um yeah that you know this involves the receptors not the growth hormone the re receptor for that’s their specialty uh we have to send a message we have to send a message to the nucleus and so then we have a whole other set of Proto
Anog genes who whose job is to send the message kind of like the telegraph system we have some of them that are located in the actual cell membrane you already know about that that’s the RAS protooncogene whose job its messenger is GTP it sends a phosphorated protein
Message and so it’s a cell membrane located messenger system then we have the ABA Al protooncogene who’s uh lives in the cytool very close to the membrane and it also uh is involved in uh in uh in messages as well um so we have to have some messenger system okay who’s the
Messenger sent to well it’s sent to a group of Proto aagen that are in the nucleus and once that message is sent to them then they uh stimulate nuclear transcription of that message in other words the cell divides and makes whatever it is it’s supposed to make the
Classic Proto alag genes there are the mick Proto genes we have enm and cmic okay en mic and cmic one’s for neuroblastoma the other one’s for Burk Loma okay so in review the uh the things the the Proto genes involved in a normal cell cell process involved those are
Make growth factors make uh growth uh receptors for those factors those that make that send messages a lot of the messages are phosphor related proteins that’s why tyosin kinas is often times attached to the receptor right off the bat so as soon as let’s say insulin for
Example hooks into a receptor on an anap POS it activates tyroine kinase we’re right on the receptor so it’s located actually right there which makes a phosphorated product which goes and does the nucleus to go divide and all that stuff and goes to the goldia apparatus and says okay guys where’s glute fors
And so they old glute Force come out that’s glucose transport units kind of like golf courts and those little those little glute fours from the ggia apparatus go to the cell membrane of the atopos and they’re The receptors for glucose okay so that’s how that works okay so the messages go to nuclear
Transcribers in the nucleus those are the MC unes okay now who’s controlling these dudes the supressor genes and we already mentioned the two most important ones the RB suppressor Gene and the p53 they’re others there are other suppressor genes but those are the most important ones they kind of control the
Cell cycle remember they try to keep it in the G1 phase so that everything can be cleaned up a little bit before it goes into the S phase and gets initiated got me so far TR to be as simple as possible okay now how do we initiate a cell mutations
For example what are the mechanisms of the m mutations not a whole lot of them actually probably the most common one’s a point mutation okay now if you don’t know what that is uh usually in Biochemistry when they do the DNA stuff and riken Bach probably is the one that does that uh
When they do that kind of stuff they talk about point mutations in the in the in those little trinucleotide things it could be substituting adenine for thyadine or something like that okay so point mutations in fact the two most important genes involved in cancer are both uh involved Point mut aut a that’s
A p-53 suppressor Gene is a point mutation that knocks that one off and then the rason gene is a point mutation that was a board question they had groups of genes and they said which ones are by point mutation okay and that was a p-53 all suppressor genes by the way
Are all point mutations that’s real easy but the other dudes the Proto gen have a couple different ones okay so rat and p53 so one thing’s point mutation that’s probably the most common another one that you’ll understand more when you get your DNA lectures if you haven’t had
Those already is what is called uh amplification it’s kind of like PCR polymerase Chain Reaction it just kind of makes multiple copies of U of U of something that’s called amplification the herb B2 uh and breast cancer is a amplification type of a system so that’s that’s a different kind of mutation but
Here’s the one you really want to remember translocation translocation that’s taking some place and putting it in another place okay right now you’ve all been translocated is this the usual place where you are no okay so you’ve been translocated over here okay you have another place that you live is that
Correct all right but unfortunately in translocation you get translocated you can’t go back you stay you want to stay here say no no okay all right now some of the classic translocations every one of them that’s importantance in your in your notes um did the big one is a chronic myologist
Leukemia is translocation of the ABA that’s non-receptor tyzine KY activity ABA from chromosome 9 to 22 and there it fuses with the brake cluster region to form this Fusion Gene then all of a sudden because it has had pyrine kinas activity it sends a message and all of a
Sudden those cells those stem cells just keep on dividing okay okay we have chronic my to course chromosome 22 with that Fusion genus called philia chromosome there you go and then we have a cancer associated with epone BL virus that translocates the mick nuclear transcriber Gene nuclear transcriber Gene from
Chromosome 8 and it sticks it on the chromosome 14 it don’t like it there and so you end up getting Burk sloma okay Burk F now if you want to understand the epon barar relationship it’s quite simple actually remember we said there’s a receptor for epon bariz and all of our B
Cells anybody remember what it’s called cd21 do you know what it does when it hooks into that receptor it causes B cells to become plasma cells and make antibody they are unbelievable stimulators of antibody synthesis so cytomegalovirus and because of the fact that it stimulates the B cell to become
Plasma cells there’s a lot of divisions that occur there guys and so isn’t it makes sense that the more a cell divides the more something bad can happen to it okay so here’s this EBV V A4 all of a sudden there’s a translocation of the MC oncogene from 8
To 14 the next thing you know you’re making multiple copies of that progression and you got yourself burgus Loma so that’s how EBV predisposes to that particular cancer it just increases the mitotic rate and it’s greater chance the greater chance you do something the greater chance you’re going to screw up
Isn’t that right that’s the same thing same thing is true with mitosis this is basically that simple okay uh 1418 translocation important that’s the one for the B cell lymphoma involving the inactivation of the suppressor Gene those are the big mutations uh there’s another one I’m blocking 1517 uh translocation for cute prog
Granul acidic leukemia anybody know what the why they’re honing in on aute prog granul acidic leukemia just for fun you can treat it with retinoic acid you can treat it with vitamin A and C the patient and even asked how does it do that the answer is it matures the blast
And so what with a malignant cell becomes benign you imagine not treating a cancer with vitamin A it’s unbelievable the same kind of stuff that you use for cystic acne you could use for treating a cancer no wonder why it’s on the exam so they ask everything about you programul acidic leukemia the
Translocation 15117 the treatment of retinoic acid every exam has it all right those are the important ones guys all right these are your suppressor genes okay they do what they’re supposed to suppress so when we knock them off then that means whatever they were suppressing keeps on going okay okay so
We we already talked about RB we talked about p53 this is the adomus polyposis Ki that’s one for familiar polyposis that’s a suppressor Gene we have the neurofibromatosis one that’s a suppressor Gene we have the wils tumor one that’s a suppressor Gene we got these dudes brca1
Brca2 okay brca1 brca2 basically both of them are involved in DNA repair okay one’s on chromosome 13 and one’s on chromosome 17 okay uh the breast cancer two is the one that’s totally associated with breast cancers breast cancer one can be breast cancer ovarian cancers and others
Okay only 15% of breast cancers have any kind of genetic relationship so most of the time they’re not genetic but these are they’re suppressor genes okay so these are the key suppressor genes over here and those are the different diseases that we see them in all right now getting out of the
Molecular level and going up to another point another another Point okay we know the mechanisms of mutations point mutations translocations uh amplification okay we know about the Proto genes can be activated by these things we know that suppressor genes can be inactivated okay who does this why did they do these
Things well you know we have three main ways chemicals viruses and radiation those are the three main ways okay now this is a trick question are you ready actually you can figure it out the answer will be obvious after I give to you which of the three is the most
Common mechanism for initiating a cell producing a mutation how many think it’s chemicals raise your hand how many you think it’s viruses raise your hand how many of you think it’s a radiation raise your hand the answer is chemicals guys smoking was the most common cause of death in the
United States polycyclic hydrocarbons of the carcinogen and smoke it’s a chemical it’s a chemical it’s even more important and more common uh more often associated with cancer than um virus induced cancer or even radiation induced cancer it’s chemicals in fact like 80% big time so don’t forget smoking
That’s the number one one it’s not just lung cancer guys it’s mouth squames of the mouth larynx lung pancreas bladder lots of things and a lot of times it’s not number one the Navy number two cervical colon leukemias holy mackel that’s a lot of cancer polycyclic hydrocarbons you
Bet okay so I’m just going to show you just a couple little picture things that relate to some of these things that that that predisposed to mutations happening this is little papillary tumor in the bladder what do you think the most common cause of that is well it’s a
Transitional cancer and what do you think the most common CA of transitional cancers are smoking but what if you worked in a d industry what would that be analine there you go what if you had wanous gr alosis you were put on a drug you ended up with um uh
Hematuria you did a cytology you saw some abnormal cells what drug was the patient on cyclopamine that’s the way they would ask it guys I know that our little our little English friend taught you about cyclop fosite and hemorrhagic cystitis okay using mesna to prevent that and I know we mentioned the fact
That it’s also a unbelievable carcinogen for transitional cell carcinoma so the way they ask it is they’ll present a case and a person with being treated with something and have a side effect and you have to tell them what the drug is in this case with psychosine that’s how they do
It okay all right here’s a lung cancer and we’re using toothpicks to hold up the main stem bronchus and of course the most common cause of this is polycyclic hydrocarbons and smoke the ones the cancers that are most often associated with smoking and main stem BR cancers
Are squamous and small cell okay here’s a virus Associated cancer here’s a do with non-tic raised red leion diagnosis come on come on Copa guys cisa me uh uh virus please herpes 8 not six not six that’s Rosa herpes eight herpes eight that’s it right there this picture has been on many many
Exams diagnosis burkus the virus epone bar virus name some other ones with epone bar virus nasio what group of people commonly Chinese okay uh liver what about liver heal C carcinoma Hepatitis B what country Asia okay because of the high is of hepatitis B and then there’s a
Certain mold in the flu name in the food named the mold aoxin B so that combination of having hepatitis B curosis plus the apoxin that’s what makes that one of the most common cancers in the Far East okay so Hepatitis B course C also can produce U
Uh liver cancer too it’s Pro some people say it’s the most common some people say it’s the second it’s kind of 4030 in terms of percentage most books that I’ve read said 40% in favor of hepatitis B and then 30% in favor of hepatitis C now somebody else might tell you the
Opposite it’s a moood point it’s a mood point I don’t think I’d worry a whole lot about that okay here some of the other viruses here okay how about HIV what’s I mean is that associated with any cancer primary cess lymphoma you want to know how they’re going to ask that
Question the rapidly increasing incidence of primary central nervous lym central nervous system lymphoma in the United States is directly attributable to the increase in AB bcde answer HIV there you go that’s how they ask a question like that got it all right okay remember also EBV for malignant
Lymphomas other than burkets as well they can do that too forget htlv one that’s not too important um herpes copes how about human papiloma virus squamous cancers cervix vagina vulva and don’t forget anus and homosexuals unprotected intercourse Common Board question okay so the same HPV you know
16 uh 18 31 that can produce cervical vaginal vulvar cancer it’s the same one that can produce uh anal squamous Cil carcinomas and homosexuals Common Board question HPV remember how that worked E6 E7 protein products E6 knocks off uh the p-53 E7 knocks off uh the retino blast that’s a
Pretty cool little virus there huh all right radiation okay this is chronic myologist leukemia over here this exact slide slide was on boards according to a few students that were taking their review in New York okay uh what is the most common cancer associated with radiation leukemia and the most common
Leukemia associated with radiation is chronic myologist leukemia that’s the one with the 922 translocation of what protooncogene ABA Al okay um this is a papillary carcinome the thyroid that’s another very big one uh for radiation induc so if they give a history of a anyone that had radiation
In the head and neck are and they say that they have uh um uh non-tender nodular masses in the cervical region that’s metastatic papillary carcinom of the thyroid related to ionizing radiation okay very very simple straightforward question okay another good one is oogenic sooma so another way they ask things is
By profession they could say which my medical profession is most subject would most likely get acute leukemia that’s the way I would ask it Radiologists okay because the most common most common uh radiation induced cancer is Leukemia who’s the ones that works most with radiation radiologist so they can ask it
That way just like they could ask yakob kitall disase what radiation or what would you generally be neuropathologist okay dealing with brains we’d have more association with brains and the prons see they do things by by where you work okay and they can ask the question all of these are in your notes
Thank you okay all right I was holding my breath that’s why I’m breathing so hard diagnosis basil cell carcinoma this exact picture has been on hundreds of exams and this is the histology they don’t when they say basil cell they mean it it means it derides in the basil cell
Layer look at that Bonk Bonk Bonk doesn’t that look like it’s just dripping off the basil cell layer you also notice it’s multifocal okay also notice this multifocal so what kind of radiation is this nonionizing radiation ionizing is the bad stuff the radiation and what is
It which UV be like is it UVA UVB or UVC b b is bad right what’s UVC not UVC UVA Woods light those of you that like Dermatology and like The flues Superficial dermatophytes okay or find shagreen Patches and tuberous sclerosis use Woods light which is called black light that’s
UVA light you beight is the stuff that you try to protect yourself from um getting uh skin cancers like basil cell most common squamous cell second most common malignant melanoma or UVB thadine diers type of that’s the mechanism of it okay so this makes sure you know the basil cell
Relationship okay here’s a precursor lesion uh for a certain cancer that’s commonly seen in Sun exposed air you can scrape it off and it comes back actinic keratosis okay what’s another name solar keratosis and what cancer does it predisposed to squamous there you go very good kind of looks pearly grayish
White and it looks like something you just scrape off and it doesn’t you can just see it to scrape off the thing but it’s it’s a dysplastic leion got squamous displasia it’s going to grow back okay and So eventually only about 3 or 4% of actinic keratosis become s with
Cancer anybody know what heavy metal predisposes to this please arsenic anybody know what countries experien a major increase in skin cancer related to arsenic Bangladesh that’s going to be a board question because it’s all over the news apparently the water supply is uh contaminated with Arsenic and all the
Arsenic related cancers are increasing that’s skin cancer that’s also going to probably be in time lung cancer it’s also probably in time also going to be angio sacoma the liver because arsenics involved in that so here’s a situation in a country where everyone’s getting exposed to it cuz it’s in the
Water so they use current events very frequently on um exam questions they do this uh this is a kid that had a wide eye reflex retinol blastoma chromosome please 13 okay is sporadic and is familial okay so how many mutations does it take for a sporadic to become retinal
Blastoma two separate ones you have to have knock one off on one of the chromosomes 13s and then one on the other one okay how many if it’s autosomal dominant genetic inheritance one you’re born with one already inactivated only there’s one more mutation on the other chromosome retinol
Blastoma is a wideeye reflex most commonly due to retinol blastoma say no no the answer is congenital cataract is the most common cause of a white eye reflex it don’t go shining your light in a little newborn’s eye and it’s white and said oh retino blastoma be calling
Everybody and this and that most commonly is due to congenital cataract which could be due to our some of those congenital infections like cytomegalovirus fella any number of those suckers so it doesn’t mean something ho home you know something that’s got to be investigated anybody know what drug is
Predisposed this to cataracts while I’m thinking about it why would a patient with with Cushings syndrome have cataracts cortical steroids they predispose to cataracts okay all right let’s break we’ll finish off NE plagia the next hour and start hematology probably a lot of good comments on that
I I saw a lot of good comments that students that took the exam had on the CU bank and they said it was the most like what their exam was of anything they ever ran across so apparently it’s got good uh got good reviews from people
That have taken the exam so it’s a good uh good product T all right genetic disease guys uh this patient wherever their Sun exposed area would be predisposed to all the skin cancers basil cell Sous cell and melanomas it’s an autosomal recessive disease name me xeroderma pigmentosum what’s the
Defect DNA repair enzymes now there’s another group of diseases that are listed in the notes that are also DNA repair enzyme things remember brca1 brca2 is involved in that so’s p-53 isn’t it splices out those defects but they are called chromosome instability syndromes they include things like U wisot Aldrich syndrome
Bloom syndrome at taxia tangc Tasia what’s another one fan con syndrome all of these have problems with DNA repair and they commonly ask these on examination so I just wanted to mention that uh there’s a basic rule of thumb it doesn’t always hold from upper lip up is
Basil cell country from lower lip down to S cell okay so I will show you when we do GI I’ll I’ll show you a Legion on the lower lip and I’m going to ask you what what odds are what is it and you should say s cell coroma if I had one on
The upper lip odds are would be basil so remember that one that was on the inside of the nose was above lip so a crater form lesion a upper lip and higher is basil cell country lower lip and lower SEL okay this basic rule of done there
Many exceptions to that but it’s it’s reasonable it’s reasonable now why am I showing this choid again with the same kind of lesion that we saw on the skin that we call the SP cell cor why why am I doing that did I make a mistake now remember we were
Talking about about spam cell carcinomas and third degree burns and spam cell caroma developing in areas of drainage from uh let’s say a sinus and there ulc that doesn’t heal with antibiotics you know so in other words with there constant irritation and there divisions of of of cells related to that
Irritation is always a greater risk for cancer and it just turns out that the most common cancer would be squamous cancer in those areas because you’re dealing with squamous epithelium not glandular epithelium this does not hold for scar cancers by the way of the lung most scar cancers that relate to Old TB
Scars or something like that or adinal coroma not squamous just holds to things on the skin okay that this relationship with Burns and um draining sinus tracts at squ coroma who can tell me the only bacteria associated with cancer he look go back to pylori name the two cancers adnoc
Carcinoma and lowgrade malignant lymphomas mhm two cancers for that sucker God I amazing little organism guys you better listen up I know for a fact this picture was on the exam cuz someone almost had a had a a contion just what’s the matter with you I my oh I
That’s might have had someone a little bit more manic than me that day okay so I know for a fact that that say on there grade in stage guys you better listen real careful big time what’s the grade of the cancer well the gr of a cancer is what’s it look
Like okay and if you can identify what it is because it’s doing something like making kedin or making glands and it’s well differentiated another term low grade if you look at something which would be most of the things that you look at it’s anaplastic highr py differentiated in other words you can’t
Tell by looking at it under the microscope what it is that’s grade that’s a grade term okay let me see if you can if you can grade these tumors now can you tell me what the origin of this is It’s gamus why because you have these beautiful carot and Pearls there
And so because you were identified it is that a low grade or a high grade cancer low grade I want you to look at that what do you see you see you see gland likee spaces right so this is an adnoc carcinoma you identified it as malignant
Glandular cells so is that low grade or high grade low grade very good so great is what it looks like now listen careful listen careful stage now I don’t want you to forget this please I want you to remember the t is in toy n is in Nancy m is in
Machine system because here’s what it does this is the most common staging system it goes from least important to most important now here’s where your problem is you think that when let’s say take breast cancer you got a breast cancer and they say that the low axillary nodes are involved okay you
Think that that’s that’s the worst thing of all no no no no no that’s the end part of tnm what’s even worse than that is if it’s out outside the lymph nodes like bone lung or liver so just because it goes to the lymph nod doesn’t mean that that’s the most important
Prognostic factor so T stands for the size of the tumor okay that thing that’s what it basically is for T stands for tumor how bigest the sucker a magic number seems to be two CET if a tumor is over two cimet It generally has a chance of metastasizing
Whenever you look at staging uh uh things for different organ two seems to always come out so do to n stands for nodes so that’s the next most important thing for prognosis is nodes the third is n that’s metastasis outside of nodes so what is the most important
Prognostic factor for cancer is a grade or stage stage and in staging what’s most important the size of the tumor whether it has lymph node involvement or metastasis to other areas metasis now let me give you an example on someone’s boards and how they screwed it up so they described their prostate cancer
They said U which of the following has the worst prognosis and they said first prostate cancer limited to the prostate then they said went into the seminal vessicles then they said went into the wall of the bladder then they said went to the lift notes around the bladder then they said went to
Bone there you go what do you think the dingdong picked the lymph notes he picked that because he didn’t know the tnm system missed it just remember tnm you can’t get screwed up if if they don’t mention something outside of the lymph nodes then the lymph nodes would be the most important
But if they mention liver bone or something like that my God that is by that’s stage four by definition okay don’t forget that very very important good Lord in heaven so let’s look at this this a colon cancer that’s a lym note okay so what’s the most important
The size of this tumor or that lymph node involvement lymph node involvement now let’s say I said that there was also a similar uh focus of uh of cancer in the liver then what liver is the most important prognostic factor very good all right host defenses you’ve had
Immunology note the most important host defense we have that little friend the cytotoxic cdat cell that is the Numero Uno most important host defense system we’ve got now we have other things macrofagos natural killer cells even says what they do natural kill okay the natural killer cells they can do that
Um antibodies by type two hypers sensitivity can do it so there’s a number of other mechanisms but numer Uno is cd8 cytotoxic t- cells why they do rounds every day looking for altered class one antigens and whenever you have a neoplastic cell those class one antigens are altered boy when that
Cytotoxic tels it gets very interested in that kills that cell okay puts puts out perforin that’s the signal for who caspases to do what apoptotically kill that cell remember has to be a signal signal to who the protasis which they call caspases and then they start breaking down the
Nucleus screwing up the mitochondria and then the cell dive without any inflammatory infiltrate whatsoever Kia you need to know on that cause and that’s tumin necrosis Factor Alpha it’s irreversible once you see this a poor patient with disseminated cancer just beginning to go into a catabolic State
You can give them total penal nutrition till it comes out of their ears they will not get their muscle mass and stuff back it’s all over that’s due to tacros factor Alpha hematology lots of different things hematologic causes of anemia are present in in malignancy for the most
Common anemia in malign most common is anemia chronic disease which we’ll discuss uh today okay that’s the overall most common but there could be other ones take colon cancer for example could be if you remember left side obstructs right side bleeds if you have a right sided colon cancer then iron deficiency
Would be more common also what if you metastasized the bone and replaced all the bone marrow that could be a mechanism or use chemotherapy drugs you know that are cell cycles specific or non-specific and you wipe out the stinking marrow you know there’s another cause of they can have autoimmune
Mechanisms with certain types of cancers but overall most commonly it’s anemia chronic disease most patient that have disseminated cancer are hypercoagulable what does that mean that means they have a tendency for forming clots of course this is a classic example the dude that has a painless
Jaundice he’s got let’s say a left super clavicular node I’m going to throw that in as a uh dis a a distractor for you has has a light colored stools and it has this peculiar uh uh lesions in in the vein that seem to jump from one part of his body to the
Next okay what’s that that’s trus soine that’s superficial migratory throof futis in the patient with carcinoma the head of the pancreas pancreatic cancers can also go to the L super clavicular node they ask the true soine very commonly they don’t say true soine they just describe this this a vascular
Problem in the veins that just kind of jumps from one place to the next it’s very pretty reasonably e comm that’s an example of a hypercoagulable state uh another thing we very commonly see with disseminated cancer is thrombocytosis and elevated plat count I can’t tell you
How many times have been asked to bone marrows on patients and say we need you to work up the cause of this thrombocytosis most of the time I can just do it from a hematology slip I see if they have iron deficiency then that’s the cause of thrombocytosis I see a scar
Over here okay thus splenectomy okay and then I look for anemias and stuff like that um and then uh to see uh if they have TB that could be another cause but when I can’t find any obvious cause for the thrombocytosis I ruled out my low proliferative diseases and stuff like
That it’s always cancer 40% of all disseminated cancers are thrombocytosis and you know what I usually find that they missed is colon cancer you want to know why and do a grand a a scho guak I said you do a St guak in this
Patient no I think I do one they do one positive colonoscopy cancer that’s the cause of thrombocytosis remember guys a stool guak is part of any normal physical exam if it’s not done you have not done a complete exam remember that always fever most common cause of fever malignancy is a gram negative
Infection usually the gram negatives of the hospital that you’re in dying eoli if you have an ining catheter if you have a respirator ponosa you have an indwelling catheter maybe in a vein or something like that uh storus with that scosi so most commonly they gram negatives
Fact the most common cause of death in cancer is infection by paraneoplastic syndromes very very important guys very very important now let me tell you what this is these are signs sometimes symptoms that that say that you may have an underlying cancer present so they kind of like little
Clues that something’s going on in a patient and why would this be important well maybe if you recognize this clue you can actually find that cancer before it’s metastasized okay so that’s that’s the key for knowing these things now listen carefully on this most common paraneoplastic syndrome is
Hypercalcemia now I’m I’m going to present two mechanisms and you’re going to tell me which one classifies as paraneoplastic remember the purpose of these things is to find some clue that will detect that will detect the cancer before it spread that’s the basic thing that was we’re saying all right there’s
Two mechanisms for hypocalcemia Lancy one is you metastasize the bone produce some kind of uh of of chemical Incan one paglen and E2 that activates osteoclast produces litic lesions and Bone waa hypercalcemia that’s one that’s the most common two it could be a couchpotato cancer like Arenal adinal coroma or
Screamous carcinoma of the main stem bronchus that just sits there and makes paraone like peptide and it just causes hypercalcemia to occur because it acts like paraon and breaking bone down a little bit which one’s paraneoplastic the second one and that’s certainly not the most common one
Okay good all right these pretty much summarize these pictures all the important paraneoplastic syndromes okay now notice there’s two lesions that are black here and both of these interestingly are phenotypic markers for the same cancer gastr adinal coroma usually this lesion this black lesion is under the arm not
Always this is called acantosis finish it nigricans okay and this is called sebri keratosis now don’t go bananas on this okay because a single sebri keratosis doesn’t mean a hill beans I got a pile of them under my uh my axelin which I’m not going to show you okay but
I mean they’re there these are these are not even neoplasms guys but here’s the thing when they suddenly develop like overnight there crops of these you know boom all of a sudden they were there that they weren’t there yesterday now they’re there that’s called the Lesser Trot sign when you get multiple
Outcroppings of these things that is a phenotypic mole for gastroc coroma so it’s kind of easy to remember because they had two black lesions predisposing not predisposing um that are markers for an underlying gastri adoc coroma I know some of you are pretty sharp and you know that a can’t those Niger can
Associated with other things I know you know about uh insulin receptor deficiency uh related to diabetes also men’s syndromes so it’s a phenotypic marker for a lot of things but most commonly gastroc carcinoma diagnosis clubbing better diagnosis hypertrophic I forget the other part of it hypertrophic whatever whatever it’s an
Inflammation underneath in the bone periostitis okay and it’s the inflammation of the under bone that stimulates increase soft tissue development around it produces the clubbing so it’s hypertropic osteopathy that’s what it is that’s what produces clubing now clubbing isn’t always associated with malignan you can see with bronch acusis uh inflammatory bowel
Disease um but if it if it were to be a malignancy would it more likely be primary lung cancer okay now this is the least common collagen vascular disease but the one most commonly associated with an underlying cancer I’ll give you a hint they have an elevation in serum
CK Gat myositis is the answer some of you should have recognized this as raccoon eyes the So-Cal heliotrope or raccoon eyes of banom monotis okay and that’s a u an inflammation of skin and muscle and so they got myositis which released the serum CK High association with leukemias and cancer lung cancer
Lymphomas Etc anybody know what the name of little patches over the knuckles and stuff like that to call Goin patches Goin patches dermatomyositis okay now we have some vegetations here on the MIT valve they’re sterile these are associated with mucus producing cancers like colon cancer okay it’s a Paran neoplastic
Syndrome this is called moranic endocarditis moranic endocarditis and U they are benign I mean they’re not not benign but they’re they’re not they’re not infected there’s no infection it just basically seems seems to be associated with mucus secreting colon cancers moranic vegetations can they embolize sure in
Fact that was a board question I mean AB ability to embolize sure because they’re pretty big I mean you can see those chipping off there now would you need some history to separate that from rheumatic fever oh you bet you would okay it looks very similar to that in
Fact looks like it’s right along the margin of the valve oh yeah no doubt about it except the history would relate more to colon cancer than rheumatic fever po arth I and stuff like that okay they would be giv US versus this okay I don’t think I would be thinking
Infective endocarditis with this because it’s too even along there infective endocarditis get these huge vegetations at different places lean Sachs not a chance lean Sachs endocarditis vegetations are all over the place including down here no way so the only thing you could potentially confuse that with is rheumatic fever that’s
It okay so those are your uh some of your paraneoplastic syndromes now the rest is up too you ready okay there’s another moranic vegetation okay these are little Snippets here and you’re going to tell me what the cancer is and where it’s located ready okay hypon neia or
Cushings lung cancer smell cell coroma hormones ADH for that act for that small cell cancer what’s another thing that’s unusual about small cells they’re output tumors S100 antigen positive neural crest origin neural secretory granules on electromicroscopy okay hypercalcemia or secondary polycythemia wrong renal adnoc carcinoma okay renal adoc carcinoma renal [ __ ] can
Make parmal like peptide and they also can make arthop okay about hypoglycemia or secondary polycythemia hpal carcinoma okay they can make arthop potin these are polysemia they can make an insulin like Factor there’s your hypoglycemia okay how about this is the hardest one actually how about hypocalcemia or Cushings I’m going to
Give you a hint there can be an autosomal dominant variety of this and this particular tumor is one of the rare tumors where the tumor marker uh can be converted into ameloid the answer is meary carcinoma of the thyroid and what was that Tuma marker that can be converted into amalo
Calcitonin there you go this is the way you ask your ectopic hormone syndrome guys if you sitting there with your fingers in your ear okay this is the way they ask them okay so this is all memorization there’s nothing there’s that you can’t think your way you can only one thing
You can think your way into and that is it’s pretty obvious to me that a kidney and cancer can produce aopo I mean that is not that’s just an absolute no- bringer all the other stuff you just have to know just absolutely memorize it there’s no no other way
Let’s see how you do on tumor Market okay what two tumor markers do you always get when you have a a male with a testicular cancer please Alpha feto protein and HCG now what is Alpha feto protein in a testicular cancer a marker for what kind of cancer yoke Sac tumor what’s another
Name for that endodermal sinus tumor now think of this guys think it this Alpha feto protein doesn’t it sound young feto protein did you know that Alpha feto protein really is the alumin of the fetus that’s really what it is and and uh so tumors in kids like of
The ovary in a girl or of the of a boy are most commonly yolk saac tumors okay Alpha fetoprotein you know young kid and even the name sounds young alphao protein okay you also know it’s associated with hpal COC carcinoma okay that’s the tumar you would want to get
To that you also know open neural tube defects it’s increased you also know that you have to be on folate before you’re pregnant to prevent open neural tube defects and you also know that in Down syndrome Alpha fetal protein down is decreased those are all the facts
That you need to know about alphao protein I want you to find for me a marker for a um malignancy of bone that’s associated with a monoclonal spike bench Jones protein and what are we talking about what disease multiple Myoma what is Ben Jon’s protein it’s the
Light chain of the amog globin very good okay I want you def find me the the tumor Mark for prostate cancer PSA is it specific for prostate cancer no why because it can be increased in hyperplasia but is it sensitive yes but is it specific no is it increased if you
Do a rectal examination absolutely not anyone that torts you otherwise is an idiot okay simply they’re an idiot want to know why it’s not an enzyme it was prostatic acid phosphatase of course this is an antigen guys it’s actually within the actual cell there is no way
That you increase it with with the rectal exam no way a lot of internist teach you oh the PSA never do a rectal exam before you’re going to get a PSA bull crap doesn’t affect it whatsoever now if it was prostatic acid F yes it would see they’re kind of confusing with
That okay please don’t fall for that mistake okay uh how about uh um breast cancer surface derived ca25 okay how about um um did I which one did I say ovarian cancer or breast oh breast no that would be 153 how about ovarian cancer ca125 199 they don’t ask
PSA alpha 1 CA how about carcino embrionic antigen what’s that for colon cancer but we also use it in small cell we also use it in breast mainly colon cancer do you know it can be part of an immune complex you can get CA anti-cea immune complexes which deposit in the
Kidney and produce nepotic syndrome name the type of nepotic syndrome please is it minimal change disease or lipoid neosis is it focal segmental glal sclerosis or is it diffuse membranous glal netis which one is it diffuse membranous glarin netis when we get to kidy we find out
That a good percentage of the nephrotic syndromes in adults well the most common overall cause is diffuse membranous chamaro nefritis but a good percentage of those are related to malignancy and one of the most common malignancy is colon cancer because CA could be the anaging part of an immune complex and
End up depositing in the gari okay if you thought uh a a woman had a trophoblastic tumor or a mole what what marker would you get bet HCG very good good very good okay I gave my last uh slide to my buddy that’s doing the uh the uh the neoplasia lectures and I
Couldn’t find another one so I’m going to just go from what I remember as the last part of the notes you ready uh what’s the most common primary Cancer all right I’m going to word it this way primary tumor of the brain and kids the answer is uh a OC cystic
Astrocytoma now now here’s what you were taught you were taught meul blastoma wrong you didn’t listen to the way I asked the question I said what’s the most common primary tumor I didn’t say whether it was benign or malignant see all astrocytomas are beny okay so the most
Common actual tumor of the brain is primary tumor of the brain is a cerebell tumor derived from asites now if I ordered it this way what’s the most common primary cancer of of the brain and a kid demil would the answer be magal blasto and again that also derives
From the cerebellum big mistake you see it wrong in lots of different books you probably said well how do you know I’m right because I checked the right books I go and I read New England Journal of Medicine I deal that with brain tumors and also uh the literature on this thing
So I’m correcting what I’m saying in fact it’s not even close cbella asroy is way way more common than meal blastomas and but they benign magical Bast what’s the most common um what are some other common childhood tumors what is the most common Childhood Cancer leukemia what leukemia specifically acute lymphoblastic
Leukemia the second group mainly is central nervous system tumors and we already know that one and then right after that we get into things like uh neuroblastomas very very common adrenal Medela and then we have burkus Lomas right up there also B cell uh e-wing suoma it’s a tumor of bone then the
Onion skinning type of calcifications that you see with that uh another another big one is the emino raddo my S coma those are the kind of the childhood ones you don’t really need to know maybe you basically need to know what’s the most common of them leukemia
Al okay now let’s deal with adults okay let’s deal with uh incidents I didn’t say cancer kill I said incidents of cancer women what’s your number one cancer breast what’s your second lung what’s your third okay men what’s our first prostate second third good notice that Colon’s third all the time all
Right now let’s talk about cancer Killers men and women okay let’s go back to men second prostate women breast third men woman trick question what’s the second most common cancer and cancer killer in men and women combined colon cancer there you go colon cancer is when you put the two of them
Together both remember we both have colons so even though they were th for the individual sex when you put a lumpus together then the second most common overall cancer and cancer killer is a colon cancer when to lump us together I actually did the math on it I looked up
Put all the numbers and added them together and it was true that’s why from age 50 on you should have a exam in a stool gak then get a flexible Sig Andor colonoscopy depending on your risk CU after 50 the most common cause of colon cancer of a of a positive spook
Wag is colon cancer your differential is colon cancer colon cancer colon cancer colon cancer colon cancer after 50 really then what’s the one after that one colon cancer okay all right um pyn cancers incidents most common most common GYN cancer leaving out breast okay your choices are cervical
Ovarian and endometrial which is the most common of the three endometrial numeral Uno numeral 2o that means number two in Spanish I know it’s not don’t worry about it some of you what’s number two ovarian what’s number three cervix why is cervical cancer the least common GN cancer patmar okay now here’s what
Some of you are thinking if you’re thinking at this particular time 11:30 but no is it that that late no that can’t be right someone change that it is that l oh my God okay here’s what you thought some of you say I don’t believe that because if you
Do a cervical cervical pack and you pick up cervical cancer would not increase the incidence but what are you picking up what why why why wasn’t that a correct statement that’s correct if that was true you’re picking up cervical dysplasia you pick up squamous cell displasia that’s not cancer and you pick
It up and then what do you do usually end up doing the cervical cone or something like that and the patient’s Cur it and because it’s cervical path smears the incidence of cervical cancer has gone down dramatically because you’re picking up the precursor lesion see initially with mamography the
Incidence of of breast cancer increased because things you couldn’t feel were now seen so the incidents went up same thing with prostate cancer and PSA now they kind of off which means we need more sensitive techniques to pick them up now okay now on cancer Killers GYN numeral Uno ovarian numeral 2 cervical
Numeral 30 and demetrial so the best way of remembering it the most common one has the best prognosis utal is the most common but it has the best prognosis okay all right what is the only known existing tumor vaccine how many of you got vaccinated against Hepatitis B all of you better
Have your hand up because if you don’t then you’re crazy okay why what is the most common infection transmitted by accidental needle stick in a hospital Hepatitis B you want to know why the viral burden of hepatitis B in the blood is greater than any infection in other words it’s
Even more more so than HIV all right so you got three things that you’re not going to get if you’ve been vaccinated one Hepatitis B what’s the other hepatitis you’re not going to get D because you need surface antigen what’s the other thing you’re not going to get heal cellular carcinoma related
To Hepatitis B related sosis three things so it’s the actually only existing tumor vaccine there is is the vaccination with hepatitis B asked all the time you just never think of it that way but it’s true did you know you can eradicate hpal COC carcinome is the most
Common cancer in the far e by simple vaccination of every one of those every one of those people you eradicate HEPA typal salor carcinoma
source